The Session Starts
Mary & John start at the same time with the same lesson. They are studying Geometry, Triangles.
Mastery learning (ML) is an educational philosophy & practice. Mastery-based learning places the emphasis on mastery rather than seat-time, which generally leads to higher proficiency and engagement levels for all learners- 98% of the learners* in the one-to-one mastery-based situation performed as well as the average learner in the traditional setting.
Mastery Learning maintains that given enough time to students according to their needs, all students have the potential achieve subject of mastery.
In mastery learning, there is a shift in responsibilities, so that student's failure is more due to the instruction and not necessarily lack of ability on his or her part. Therefore, in a Mastery Learning environment, the challenge becomes providing enough time and employing instructional strategies so that all students can achieve the same level of learning.
*1984 educational psychologist Benjamin Bloom report in his famous 2 Sigma Problem paper in published in ‘Educational Researcher’ All students have the potential to succeed. All they needs is an opportunity to learn in their own way, at their own pace and skill level
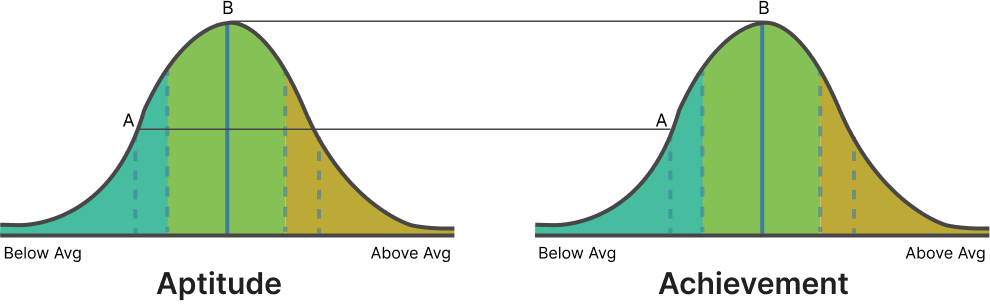
| Outcome | Aptitude | Achievement |
| Student A | Below Average | Average |
| Student B | Below Average | Average |
Outcome: Performance is in accordance with the aptitude*
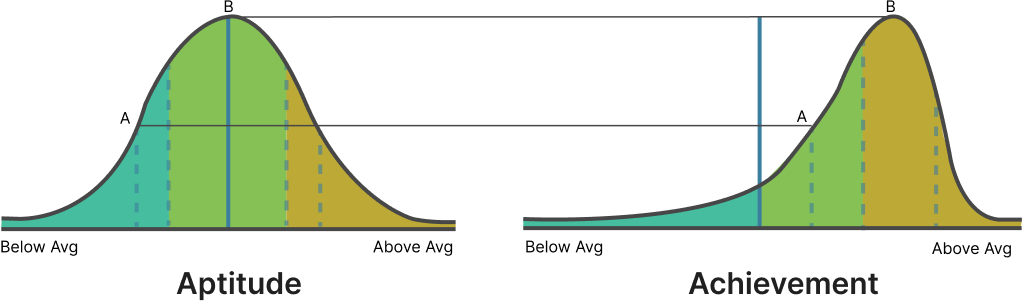
| Outcome | Aptitude | Achievement |
| Student A | Below Average | Average |
| Student B | Average | Above Average |
Outcome: Performance is disproportionately higher for majority of the students
The best way to figure out how things works is to disassemble the whole thing; understand each part and how each part connects with the other parts. Once you know everything, it is easy to put it all back together.
Mary & John start at the same time with the same lesson. They are studying Geometry, Triangles.
They use various inputs to study the subject matter in the class.
Having completed the Study & Practice sessions they are ready to take a Formative Assessment.
Mary successfully completes the assessment. John Falls short.
Mary needs to move on to the next lesson. John needs to take a step back and revisit the Triangles.
Mary and John started with the same lesson at the same time but now they need to study different lessons based on their skills and speed, although they are in the same class.